Retrieving horizon data
Virtual Horizon acts as a digital assistant, extending the driver’s location context beyond their immediate view. It can be used by UI components to improve the driving experience, for example, by informing the driver of what is ahead. This information includes details about upcoming traffic events, vehicle restrictions, and more.
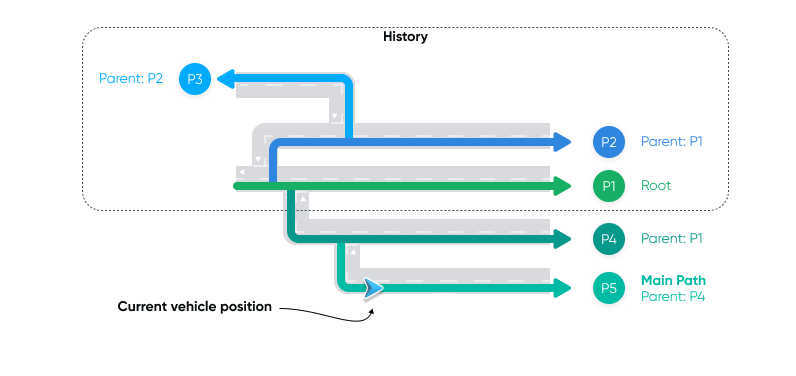
While navigating, you can use Virtual Horizon to retrieve detailed information about the horizon ahead of the vehicle, along the possible trajectories of the vehicle across the road network. Horizon data is delivered to your application as a combination of a HorizonPosition and a HorizonSnapshot .
The SDK provides horizon data for various elements, including:
-
StreetElement- Information about a street, such as name. -
SpeedLimitElement- Information about speed limits. -
GeneralRoadPropertiesElement- Information about the road ahead, such as number of lanes, functional road class and driving side. -
CountryInformationElement- Information about the country ahead, including country code, speed limit unit, regional speed limits, etc.. -
CityElement- Information about the city ahead, such as its name. -
RailwayCrossingElement- Information about upcoming railway crossings.
This guide focuses on demonstrating how to obtain speed-related data — the current speed limit, the distance to the next speed limit, and the value of the upcoming speed limit — using the public navigation APIs. These insights allow you to create navigation applications that not only guide users accurately but also keep them well-informed.
For more in-depth information, refer to the horizon data types, such as HorizonPosition and HorizonSnapshot .
Configuring horizon
Incorporating horizon data into your navigation application requires the following steps:
- Define your horizon data preferences by specifying
HorizonOptions. - Add a
HorizonUpdatedListenerto receive data based on your chosenHorizonOptions. - Start navigation with or without a route as described in the Starting navigation guide .
Specifying horizon options
First, define the set of HorizonOptions . To indicate that you are interested in SpeedLimitElement horizon elements, specify SpeedLimitElementType in the list of element types of interest. The horizon path parameters defined within buildHorizonOptions are appropriate for most use cases and can be utilized in both free driving and active guidance scenarios. The buildHorizonOptions method will create a HorizonOptions instance with a main path search distance that is the minimum between 25 km and the remaining route length when navigating with a route, or 10 km when free driving.
private val horizonOptions = buildHorizonOptions(listOf(SpeedLimitElementType)) When using the Extended flavor
If you prefer to configure the horizon path parameters manually, you can create the HorizonOptions as follows:
val horizonOptions = HorizonOptions( elementTypes = listOf(SpeedLimitElementType), mainPathSearchOptions = MainPathSearchOptions( searchDistancePolicy = ExplicitDistancePolicy( searchDistance = PathSearchDistance( maxHorizonLength = Distance.kilometers(1), ), ), ),)Starting navigation
To start navigation with a route, follow the Starting navigation guide .
But, instead of adding a listener for route progress updates, make sure you add a HorizonUpdatedListener to listen to horizon updates. You’ll need to use the HorizonOptions returned from the buildHorizonOptions method to subscribe for horizon updates in the listener.
fun startNavigation() { tomTomNavigation.addHorizonUpdatedListener(horizonOptions, horizonUpdatedListener)
val routePlan = RoutePlan(route, routePlanningOptions) val navigationOptions = NavigationOptions(routePlan) tomTomNavigation.start(navigationOptions)}Retrieving horizon data
With navigation started, you can listen to horizon updates and retrieve horizon data.
private val horizonUpdatedListener = object : HorizonUpdatedListener { private var horizonSnapshot: HorizonSnapshot? = null
override fun onPositionUpdated( options: HorizonOptions, position: HorizonPosition, ) { horizonSnapshot?.let { snapshot -> position.takeIf { it.isOnRoad }?.let { position -> snapshot.displayCurrentSpeedLimit(position) snapshot.displayNextSpeedLimit(position) } } }
override fun onSnapshotUpdated( options: HorizonOptions, snapshot: HorizonSnapshot, ) { horizonSnapshot = snapshot }
override fun onHorizonReset(options: HorizonOptions) { // do nothing } }Once you have retrieved the data, you can use it to extract the value of the current speed limit.
private fun HorizonSnapshot.displayCurrentSpeedLimit(position: HorizonPosition) { mainPath()?.getElements(SpeedLimitElementType) ?.firstOrNull { element -> element.startOffset < position.offset && element.endOffset >= position.offset } ?.let { element -> (element as SpeedLimitElement).speedLimit } ?.also { speedLimit -> when (speedLimit.type) { SpeedLimit.Type.Limited -> Log.v(TAG, "Speed limit value: " + speedLimit.speed) SpeedLimit.Type.Unlimited -> Log.v(TAG, "Unlimited speed") } }}You can also extract the distance to the next speed limit and the value of the next speed limit.
private fun HorizonSnapshot.displayNextSpeedLimit(position: HorizonPosition) { mainPath()?.getElements(SpeedLimitElementType) ?.firstOrNull { element -> element.startOffset >= position.offset } ?.let { element -> Log.v(TAG, "Distance to the next speed limit: " + distanceTo(element, position)) (element as SpeedLimitElement).speedLimit } ?.also { speedLimit -> when (speedLimit.type) { SpeedLimit.Type.Limited -> Log.v(TAG, "Next speed limit value: " + speedLimit.speed) SpeedLimit.Type.Unlimited -> Log.v(TAG, "Next, unlimited speed") } }}Next steps
Now that you know how to retrieve horizon data, here are the recommendations on what to explore next: